Issue 12/2025
Peev, K.
University Hospital “St. Anna” – Sofia
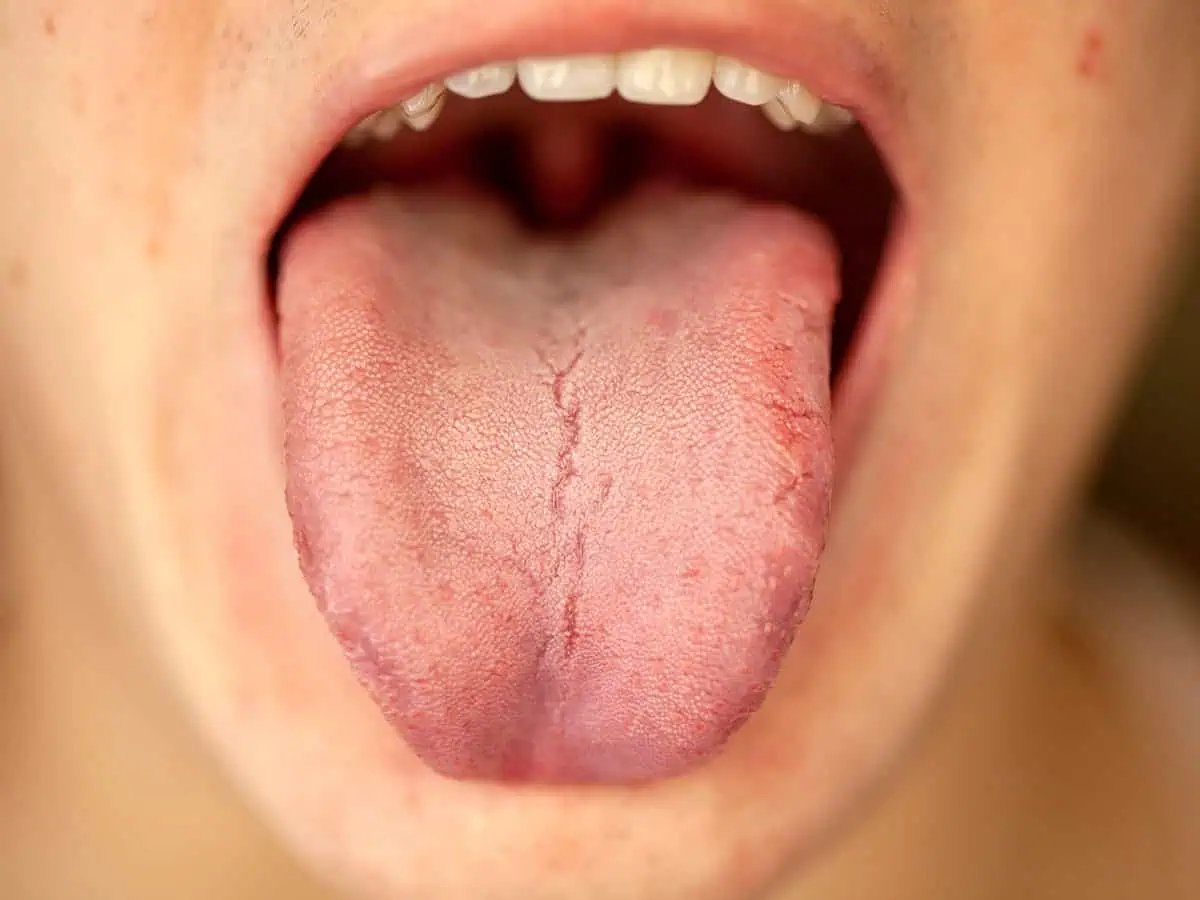
Glossitis is an inflammatory condition of the tongue, which manifests itself with erythema, edema, pain and often – loss of lingual papillae. The tongue is a highly specialized organ with an important role in taste perception, articulation and digestion, and its rich blood supply and innervation make it vulnerable to various pathological processes. The etiology of glossitis is multifactorial and includes infectious (candidiasis, bacterial, viral), traumatic, nutritional (vitamin B12, folate, iron deficiency), immunomediated and dermatological diseases, as well as systemic conditions such as anemia, diabetes, malabsorption and GERD. Some forms, such as geographic tongue and median rhomboid glossitis, have a characteristic clinical appearance, while persistent ulcers or infiltrative lesions require the exclusion of neoplasia.
The clinical picture is characterized by pain, burning, depapillation, dysgeusia and candidiasis-like plaques. The diagnostic approach includes a detailed history, examination of the oral cavity, laboratory tests, microbiology and, if necessary, biopsy. Treatment is etiological – correction of irritants, local and systemic therapy for infections and deficiencies, as well as treatment of underlying diseases. Knowledge of the different types of glossitis is key for early diagnosis and proper behavior in local and systemic pathologies.
Keywords: glossitis, glossitis
